Air Conditioning System Operation -By San Antonio Techs
At Auto Service Experts San Antonio Auto AC Repair Shop, our ASE Certified Master Technicians take time to explain how your vehicle’s AC system works in clear, easy-to-follow language. We want you to understand what we found, what it means, and what your options are, so you can approve your auto AC repair with confidence.
Car AC Components and How They Work To Keep You Cool
Refrigerant / Freon

An AC refrigerant recharge should only be performed by a professional technician using specialized equipment that recovers & recycles refrigerant, minimizing environmental damage.
AC refrigerant is a chemical compound that absorbs and transfers heat in a refrigerant cycle. It is commonly referred to as Freon, which is a trademark name. An automotive air conditioner incorporates several components that work together to circulate, compress, cool, and condense refrigerant.
Refrigerant is changed from a gas or vapor state into a liquid state, then back into gas in a continuous cycle. R-12 refrigerant was used in most vehicles until it was banned in 1994 and replaced by the more environmentally friendly R-134a refrigerant. Today’s automobile manufacturers (including GM) are beginning to use HFO class refrigerants such as R-1234y & R-744 which offer increased energy efficiency. They are more cost effective and have less of a harmful effect on the ozone layer, therefore contribute less to global warming.
AC Compressor
The AC compressor is sometimes referred to as the heart of a car’s air conditioning system because it supplies the system with Freon, or the blood. This liquid refrigerant that is pumped into the compressor in gas form through the suction port. This gas is then pressurized within the discharge port. The compressed Freon is circulated through a series of different-sized cylinders and hoses, which create alternating vacuum and pressure, and an expansion valve designed to make the gas contract and expand. Some compressors have a rotary/vane design, and others use pistons and rods to connect to the main shaft. Compressors receive power from a drive belt in the engine. Controls moderate pressure and cabin temperature inside the compressor, and refrigeration can be turned on or off by an engagement clutch which is electrically controlled.
AC Condenser
From the compressor, the gaseous Freon is pumped into the condenser. The condenser uses the engine fan’s cold air to reduce the temperature of the gas and turn it back into liquid. This liquid flows through a filter which collects all foreign contaminants, into receiver-driers (Expansion Valve System), or accumulators (Orifice Tube System), where it is stored.

Nissan Repair at Auto Service Experts – Compressor Kit Replacement on Nissan Rouge
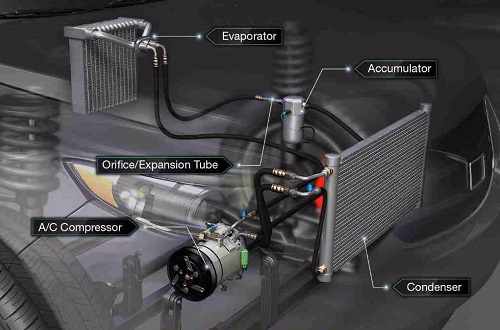
Orifice Tube System / Accumulator
The orifice tube system is designed to keep refrigerant from flooding the evaporator or entering the compressor in liquid form. These systems control the flow from the accumulators to the evaporator. AC accumulators trap moisture within the system, and clean and store refrigerant. The orifice tube changes Freon from high-pressure liquid into low-pressure liquid and supplies only a mist of refrigerant to be evaporated back into gas. The orifice tube system is found in most domestic cars, trucks, and SUVs.
Expansion Valve System / Receiver-Drier
Most foreign or import vehicles are equipped with an AC expansion valve system which takes the place of the orifice tube system. The systems use receiver driers instead of accumulators, which are very similar in operation and function, with the major difference being where they are located within the air conditioning system. A receiver-drier is connected on the high-pressure side, and an accumulator is on the low-pressure side.
Evaporator
Compressed refrigerant is transferred from the condenser to the evaporator. Excess condensation is allowed to escape the evaporator through a drain tube. This condensation can be seen dripping beneath the vehicle and may leave a substantial puddle. This is normal, although it is sometimes mistaken for an AC Leak. From the evaporator, the gaseous freon returns to the suction port of the compressor to repeat the process.
Air Conditioner Components That Periodically Need Service
Common Car Air Conditioner Problems often involve repairs or replacements of one or more of the following components:
- Compressor
- Condenser
- Liquid Line
- Orifice Tube
- Receiver/Drier
- Accumulator
- Control Head
- Low Pressure Switch
- Amplifier
- Ambient Temperature Sensor
- Dual Climate Control
- Evaporator
- Cabin Filters
- High-Pressure Switch
- Vintage Air
- Manifold Hoses
- Blend Door Actuators
- Evaporator Cases
- R-12
- 134-A
- Retrofit
- High and Low Fittings
- Blower Motors
- Relay
